Small cells are access points for devices that connect to wireless networks operated by telecommunications and internet service providers. Wireless service providers will deploy a small cell antenna to close coverage gaps in their existing networks, increase network capacity in high-demand areas and meet the growing data demands of new technologies.
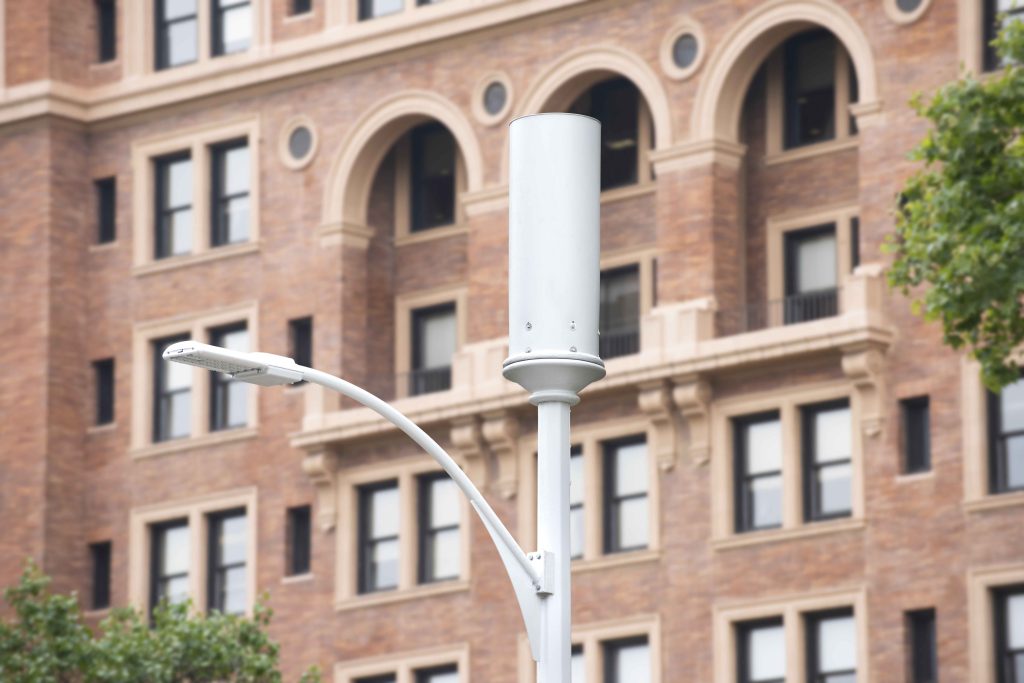

Unlike the large macro towers with long-range antennas that were built to create the first wireless networks, small cells consist of low-power short-range radio antennas and related equipment mounted at heights of 50 feet or less. Small cells are typically attached to infrastructures such as streetlights, utility poles, or building walls allowing a more discrete installation while providing better connectivity. As wireless carriers seek to ‘densify’ existing wireless networks to provide for the data capacity demands of “5G”; small cells are viewed as a solution to increasing cellular network capacity, quality and resilience with a growing focus using LTE Advanced
5g Small Cell Antenna Future
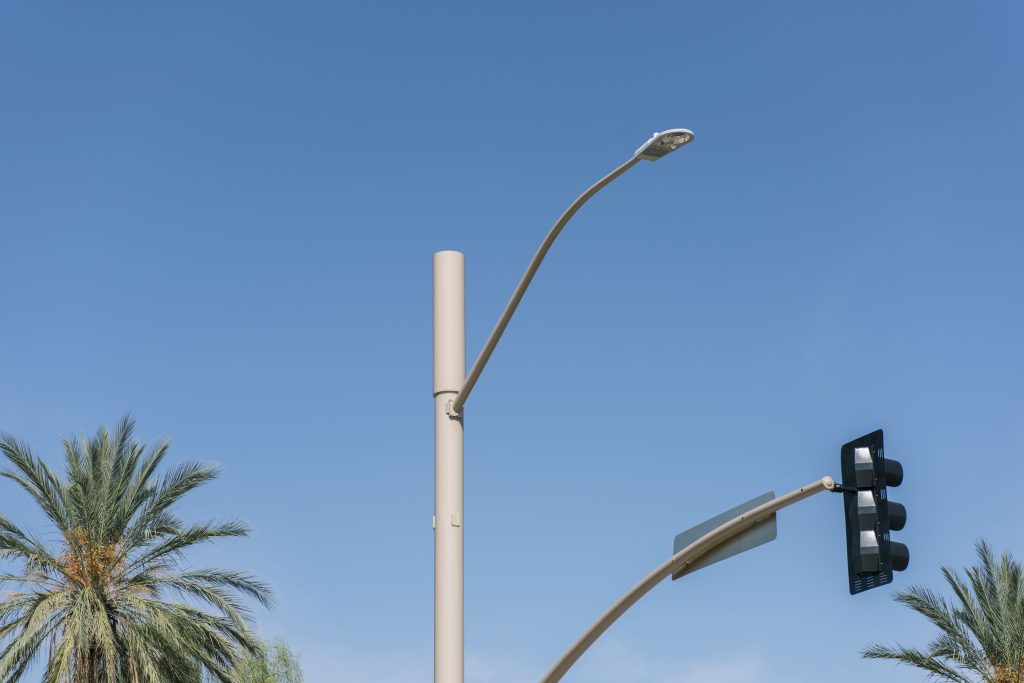

5G small cell antenna and wireless services will transform the economy through increased use of high-bandwidth and low-latency applications. While the existing wireless infrastructure was established primarily using macro cells with relatively large antennas and towers, wireless networks increasingly have required the deployment of small cell systems to support increased usage and capacity. This trend will increase as demand continues to grow, and providers deploy 5G service across the nation.
Will small cell antennas replace cell towers?
The current answer is no, however, they will reduce the number of towers and rooftop antennas needed in an area. Small cell antennas are not a replacement for cell towers but an added feature to increase speed and support demand. Wireless Carriers have not begun decommissioning any macro cell tower sites and they continue to add tower locations across the country. However, the consolidation into co-location sites along with small cell atennas will reduce the demand for large tower locations.
Regulation of Small Cell Antenna Sites
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) serves as the regulating authority for all radio, television, wire, satellite, and cable communications throughout the United States. The FCC creates rules and regulations applicable to small cells such as allocating the frequencies they operate on, setting safety limits for human exposure to radiofrequency emissions, and certifying that equipment used by wireless providers meets safety standards. As part of a national initiative to accelerate the deployment of small cell infrastructure, the FCC created regulations that govern the state and local government permit procedures. A small cell antenna on a utility pole can also be regulated by local planning departments, especially with the new 5g small cell antenna.